Tag: Haemorrhage
-
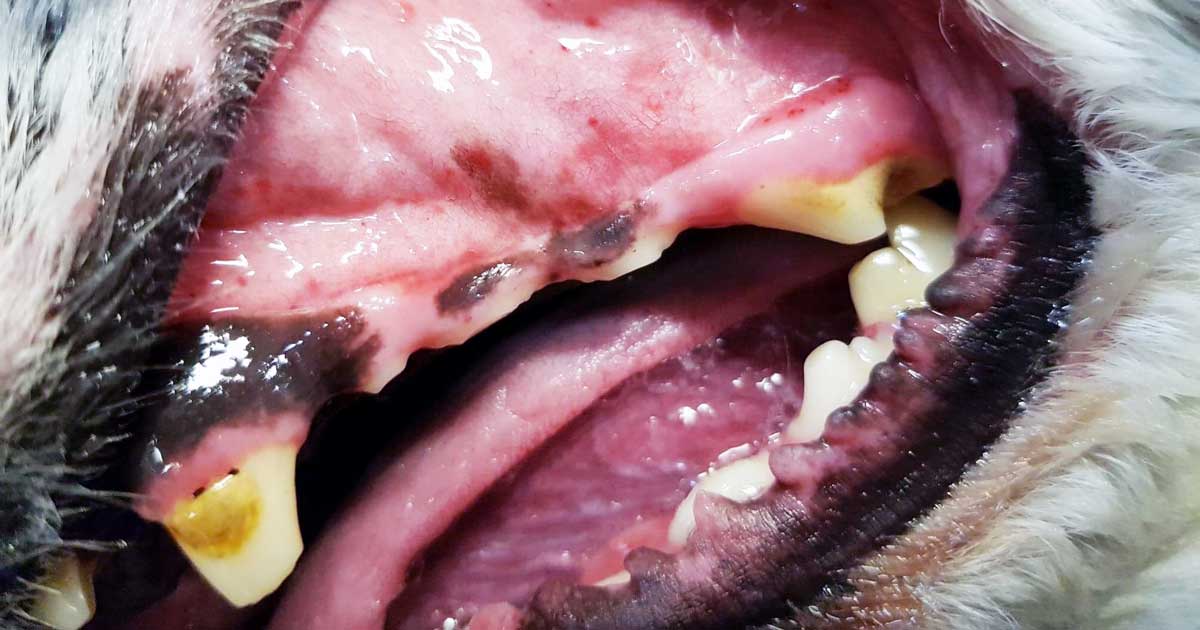
Managing thrombocytopenia in cats and dogs: part 2
—
by
Last week we discussed the causes and diagnostic pathway for investigating immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. This week we will go through the management of this condition. Despite the fact red blood cells are not actually being destroyed, a severe anaemia can develop from blood loss due to coagulopathy – a common reason for why they present to…
-
Managing thrombocytopenia in dogs and cats: part 1
—
by
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterised by a decrease in platelet numbers, which is often caused by increased destruction of platelets or a decrease in production. Thrombocytopenia can manifest in many ways – the signs can be subtle and easily missed, such as small petechiae on gums, or quite obvious signs, such as large areas of…
-
Dystocia, pt 2: diagnostics
—
by
Part one of this series covered the stages of labour and indications dystocia is present. Once the bitch presents to the clinic, a few basic diagnostic checks need completing to determine the status of the bitch/queen and the fetuses. Physical examination The first is a thorough physical examination, starting with the bitch or queen: Demeanour,…
-
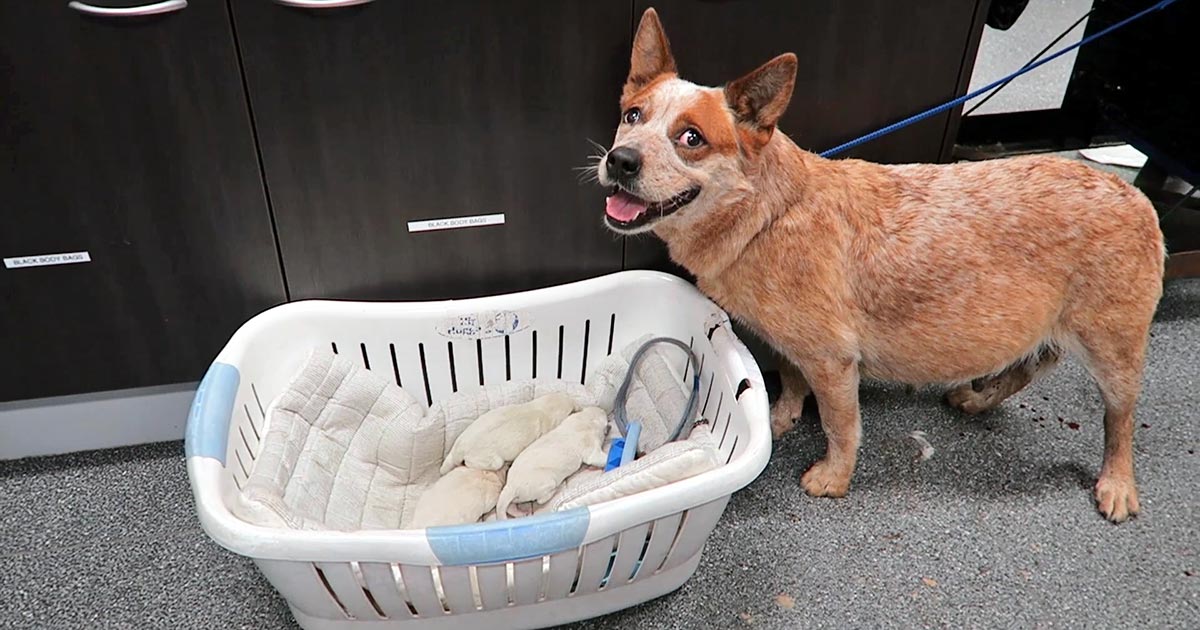

Dystocia, pt 1: labour stages
—
by
Now most female canine patients are spayed, it comes as no surprise reproductive emergencies are not as common. One confusion seems to be not knowing how to determine a true dystocia emergency – especially when given advice over the telephone – from the process of normal parturition. Another concern is how to confidently form a…
-
Thoracentesis, part 2: sample work
—
by
Last week we gave some hints and tips about how to perform a thoracocentesis. This week we look at what to do with the sample you collected and where to go to next. Looking at the sample is not enough, there are several things you need to do to make sure you are getting the…
-
Seizures, part 1: the questions to ask
—
by
Clients often panic when they think their pet is having a seizure and can skip over vital information. Often, what an owner describes as a “fit” may actually be syncope, collapse from anaphylaxis or internal haemorrhage (for example, neoplasia), a vestibular event or a behavioural condition. True seizures True seizures can be divided into two…
-
Systemic hypertension, part 1
—
by
Blood pressure monitoring is a standard practice as part of human medicine physical examination. In veterinary medicine, however, this is often omitted due to patient compliance issues, as well as inaccuracy as a result of transient hypertension caused by stress and fear. Systemic hypertension ultimately results in target organ damage – brain, heart, kidneys and…
-
Catharsis, enemas and colonic irrigation for acute oral poisoning
—
by
Great news for those who hate enemas: you may not have to do any of these ever again. This is the consensus by both the American Academy of Clinical Toxicology, and the European Association of Poisons Centres and Clinical Toxicologists. The theory behind these procedures is legitimate – reducing systemic exposure of a toxicant by…
-
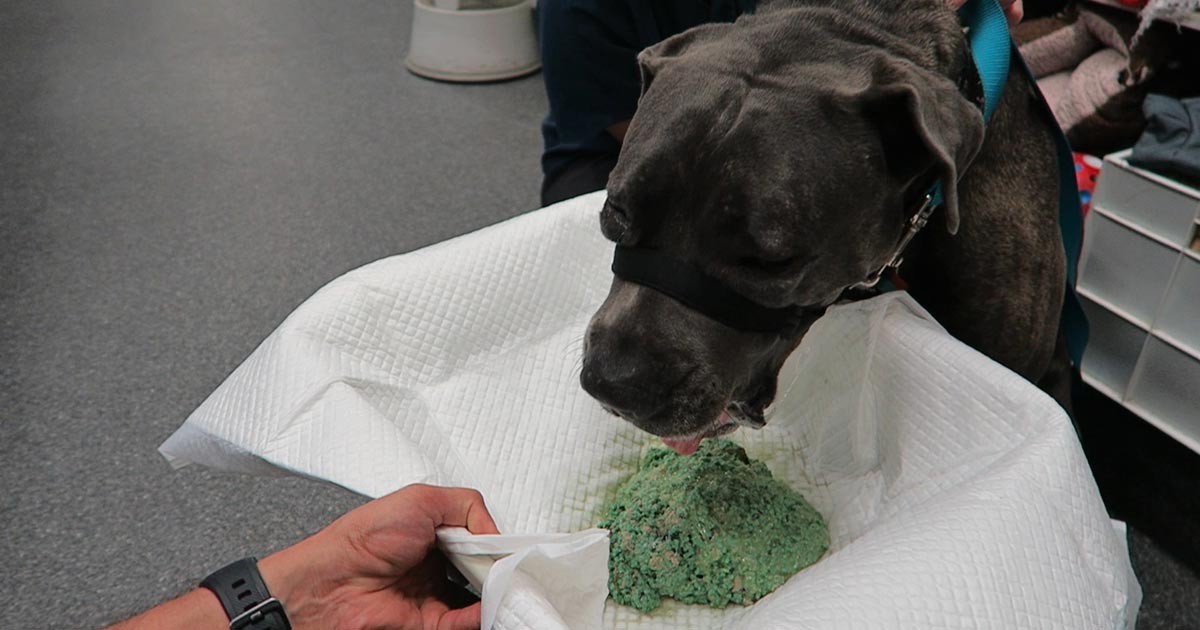

Emesis: a thing of the past?
—
by
Until I started researching this Tip of The Week, I did not know the medical profession has abandoned the routine use of emesis in oral poisoning. This is based on multiple medical literatures that have proven emesis induction does not influence the clinical severity of poisoning, the length of hospitalisation and the clinical outcome or…
-
Making sense of effusions (part 2): effusion analysis
—
by
Last month we talked about how to determine if your effusion was septic. This time, let’s look into further evaluation of effusion samples. If the effusion is haemorrhagic, here are some things to look out for. Real or iatrogenic origin? Blood rapidly defibrinates in cavities – so if it clots, it is iatrogenic. If it…